normal endometrial thickness measurements premenopausal|endometrial lining thickness chart normal : vendor The normal thickness of the endometrium can range up to 15 mm. This is measured with the uterus in profile or longitudinal dimension on a transvaginal scan. . WEBThis is a categorized list of notable onion services (formerly, hidden services) [1] accessible through the Tor anonymity network. Defunct services and those accessed by deprecated .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Laboratório Clínico - Exames – Hemolabor
Premenopausal. In premenopausal patients, there is significant variation at different stages of the menstrual cycle. during menstruation: 2-4 mm 1,4. early proliferative phase (day 6-14): 5-7 mm. late proliferative / preovulatory phase: up to 11 mm. secretory phase: 7-16 .
silver bear 62 gr 223 soft point gel test
endometrial thickness in the secretory phase (days 14-28) may normally be up . The median ET was 8.6 mm (90% and 95% quantiles: 13.8 and 15.8 mm). The ET was not related to their age, symptoms, obstetric history, geographical location, or risk factors .In premenopausal patients, there is significant variation at different stages of the menstrual cycle. during menstruation: 2-4 mm 1,4. early proliferative phase (day 6-14): 5-7 mm. late .
The normal thickness of the endometrium can range up to 15 mm. This is measured with the uterus in profile or longitudinal dimension on a transvaginal scan. . Endometrial thickness can change throughout a person’s life, such as during pregnancy or menopause. Learn what is typical and how to measure endometrial thickness here. The median ET was 8.6 mm (90% and 95% quantiles: 13.8 and 15.8 mm). The ET was not related to their age, symptoms, obstetric history, geographical location, or risk factors .
In premenopausal women, endometrial thickness is used to monitor infertility treat ment, while in postmenopausal women with abnormal uterine bleeding it is useful as an initial investigation .
In premenopausal women, endometrial thickness is used to monitor infertility treatment, while in postmenopausal women with abnormal uterine bleeding it is useful as an initial investigation .
Endometrial thickness should raise suspicion at cut-offs of > 5 mm by SRU and > 4 mm by ACOG guidelines for symptomatic postmenopausal women and ≥ 11 mm for .
The uterine lining is called the endometrium. During an imaging test, it’ll show up as a dark line. This is the “endometrial stripe.” Here’s how this tissue can change with age, symptoms .The designation of normal limits of endometrial thickness rests on determining at which thickness the risk of endometrial carcinoma is significantly increased. Whilst quantitative assessment is important, endometrial morphology and the presence of risk factors for endometrial malignancy should also be taken into account when deciding whether or . We sought to determine an endometrial thickness measurement that should be considered abnormal and therefore prompt biopsy in a postmenopausal woman without vaginal bleeding. . (> 11 mm). In a woman without bleeding, if the definition of a normal endometrial thickness is lowered from 11 to 7 mm (so that a measurement of 8 mm or greater would .
The normal thickness of the endometrium. . Menopause: After menopause, the endometrium usually measures 5mm or lesser in healthy individuals. How to measure endometrial thickness? Ultrasound is the easiest and most common method to take measurements. When ultrasound is not suitable due to the position of the uterus etc., doctors . Through multicenter trials and retrospective meta-analyses, an endometrial thickness of 4 mm has been well established as the threshold above which endometrial sampling should be considered. With an endometrial thickness of 4 mm or less, the negative predictive value for endometrial cancer is greater than 99%. Smith-Bindman et al conducted a .
The endometrium of the ovulating reproductive-age woman fluctuates in single-layer thickness from 2 mm in the early follicular phase to 6 mm in the late luteal phase. Typically, endometrial thickness is actually measured and reported as the sum of the two adjacent layers of the endometrium, a measurement called the endometrial echo complex (EEC).A transvaginal ultrasound exam may be done to measure the thickness of the endometrium. For this test, a small device is placed in your vagina. Sound waves from the device are converted into images of the pelvic organs. If the endometrium is thick, it may mean that endometrial hyperplasia is present. . Menopause is confirmed after 1 year of .ment of the endometrium is made at its maximal thickness on a midline sagittal image of the uterus obtained by transvaginal ultrasound. It is a bilayer measurement com-bining the width of both the anterior and the posterior layers of the endometrium. It has been suggested that the normal endometrial thickness in a postmenopausal woman is 5 mm. The endometrium lines the uterine cavity. Endometrial thickness is a standard measurement in ultrasounds of the pelvis. There is a range of thickness depending on whether the women is premenopausal or post menopausal. The normal thickness in women who undergo menstruation depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
The endometrium demonstrates a wide spectrum of normal and pathologic appearances throughout menarche as well as during the prepubertal and postmenopausal years and the first trimester of pregnancy. Disease entities include hydrocolpos, hydrometrocolpos, and ovarian cysts in pediatric patients; gestational trophoblastic disease during pregnancy; .
THE PREMENOPAUSAL ENDOMETRIUM The detection of an abnormal endometrial thickness in pre menopausal women is usually not a cause for alarm. The endometrial thickness in premenopausal patients varies with the menstrual cycle. In one small series of patients, 10 a range of 6-12 mm was considered to be normal. Similar findings were
endometrium thickness chart stages ultrasound
Endometrial biopsy is a safe, efficient, and cost-effective method for evaluating the endometrium. 1, 2 This office procedure is commonly performed for evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding and .Ultrasound (US) images of the pelvis were evaluated in 112 asymptomatic postmenopausal women to investigate the normal range of endometrial thickness (double-layer measurement) and the effect of hormone replacement on these measurements. Twenty-one patients (19%) had endometrial thickness greater th . this technique has a negative predictive value approaching 100% for the exclusion of endometrial cancer - however sensitivity depends on the cut-off used for normal endometrial thickness (2) meta-analysis of 35 studies (using a 5mm threshold to define abnormal endometrial thickening) reveled that around 96% of women with cancer had endometrial .
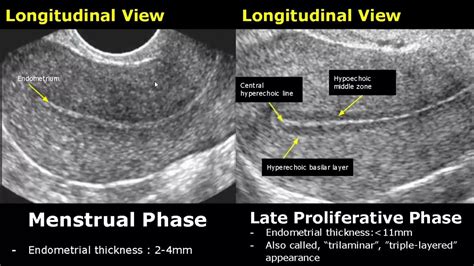
Sagittal images of four different patients demonstrate the normal premenopausal appearance of the endometrium at various stages of the menstrual cycle. . Peeters JA, Opmeer BC, et al. (2012) Capacity of . Measurement of endometrial stripe thickness (ET) is taken as the anterior–posterior dimension of the endometrial stripe on a long-axis image of the uterus. . Premenopausal: ≤ 3 cm is normal, > 3 cm to ≤ 5 cm (≤ 7 cm for superior visualization) is described to document with no follow-up, > 5 cm (> 7 cm for superior visualization) needs .3.2. The Thickness of Endometrium before Treatment and 1 Month, 2 Months, and 3 Months after Treatment. Before treatment, there exhibited no significant difference in endometrial thickness (P > 0.05).The thickness of endometrium in the study group after 1 month, 2 months, and 3 months treatment were remarkably thinner than that before treatment (P < 0.05), and .the cut-off value of endometrial thickness (ET) to exclude endometrial disease in premenopausal women in office gynecology and, as a first step, it was thought to be essential to determine the median ET of general premenopausal women who attend office gynecology. In ad-dition, it was thought to be useful to determine the upper limit of the
As a woman's age increases, her risk of cancer increases at each endometrial thickness measurement. For example, using the 11 mm threshold, the risk of cancer associated with a thick endometrium increases from 4.1% at age 50 years to 9.3% at age 79 years.
Fig. 1. Pitfalls in evaluating the endometrium. A Incorrect measurement of the endometrium. The sonographer mea-sured the median echogenic layer (arrow) of the trilaminar endometrium, underestimating the thickness. B Incorrect measurement of the endometrium. Echogenic fluid (arrow)is present within the endometrial cavity and was included in the Learn about normal and abnormal endometrial thickness in this article. . It all depends on the stage of her menstrual cycle when the measurement is taken. 2 mm to 4 mm during the periods. . Postmenopausal-Following menopause, the endometrium's thickness stabilizes. The average stripe is thinner than 5 mm in menopausal women who still .
Natural cycle preparation for embryo transfer, which allows for normal endogenous estrogen production, is an option that is gaining favor among ovulatory women, although whether the endometrial lining is improved among women with a thin endometrium has not been fully studied. . Endometrial thickness measurements among Asherman syndrome .Summary: Endometrial hyperplasia is defined as irregular proliferation of the endometrial glands with an increase in the gland to stroma ratio when compared with proliferative endometrium. Endometrial cancer is the most common gynaecological malignancy in the Western world and endometrial hyperplasia is its precursor. In the UK, 8617 new cases of endometrial cancer .
This article will discuss normal endometrial thickness, what instigates changes, and when it becomes a matter of concern. . the endometrium changes in size due to the impacts of menopause. Typically, the endometrium is the thinnest during menstruation. . the maximum measurement of a healthy endometrium is generally considered at a threshold . The endometrium is a dynamic target organ in a woman’s reproductive life. It undergoes cyclical change regulated by the fine balance between oestrogen and progesterone. The endometrial thickness (ET) varies according to the phases of the menstrual cycle. Endometrium contains both oestrogen and progesterone receptors, which respond to above .
Which of the following endometrial thickness measurement represents the upper limit of normal in the premenopausal patient? 14 mm. A 72 year old female presents with bleeding. The sonographer notes an endometrial thickness measurement of . The normal endometrial thickness measurements are : STAGES THICKNESS; During menstruation: 2 – 4mm: Early proliferative phase (day: 6-14) . Endometrial disorders such as cancer can produce thickened endometrium in non-pregnant women. Menopause is the most prevalent and natural cause of endometrium thinning.
endometrium thickness chart post menopause
WEBGRAB HERE. 18+. Prizes: Free Spins, Casino Bonus, Free Bets, Free Bingo Tickets, Coral Coins and £500 Cash (Golden Rewards Grabber only). Accept prizes within 48 hrs and use within 7 days. Max 1 grab per player/day. Some prize restrictions apply. Player restrictions and T&Cs apply. FREE-TO PLAY. DAILY CASH PRIZES.
normal endometrial thickness measurements premenopausal|endometrial lining thickness chart normal